 Michael Chissick has been teaching yoga to children in primary mainstream and special needs schools as part of the integrated school day since 1999. He is a primary school teacher as well as a qualified yoga instructor. He is also a specialist in teaching yoga to children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Michael trains and mentors students who want to teach yoga to children.
Michael Chissick has been teaching yoga to children in primary mainstream and special needs schools as part of the integrated school day since 1999. He is a primary school teacher as well as a qualified yoga instructor. He is also a specialist in teaching yoga to children with Autism Spectrum Disorders. Michael trains and mentors students who want to teach yoga to children.
Michael is the author of the forthcoming children’s book, Frog’s Breathtaking Speech, which teaches four yoga breathing techniques in a fun and interactive way and shows how they can be used to deal with anger, anxiety and tension.
In this interview, he shares the story of how this beautiful book came to be and the rewarding experiences he’s had teaching yoga to children; why he believes children nowadays need tools to cope with life’s stresses more than ever before; and how the breathing techniques in the book can be used with all children, including those with special needs.
Tell us a bit about you – how did you get into yoga, teaching yoga and teaching yoga to children?
I first came to yoga in 1974, and although I practised regularly it was not till 1990 that I consciously stepped up my practice and interest.
In 1990, following the death of my wife Jill, I decided to give up my business and look after my children. I made up my mind that Jill’s death would not be wasted and that I would do something meaningful with my life. I signed up to an Access Course, which got me back into studying and prepared me for University. As a mature student I simply thrived on the course and it unleashed a creative side of me that I had never known before. I went on to take a four year degree course in Education, (BEd Hons) and eventually took up my first post as a primary school teacher in Old Harlow, Essex, UK at the age of forty-six.
It was during my four year degree course that I established my deep interest in children’s self-esteem – specifically how it can be damaged and how it can be improved. Of all the areas that I studied this was for me the most important and I determined to make enhancing children’s self-esteem the core of my approach to teaching.
In the nineties yoga was such an essential part of my life that soon I had completed my yoga teacher training with the British Wheel of Yoga, and was able to begin my new career teaching yoga to adults. It was an obvious next step to merge my skills and experience as a primary teacher and qualified yoga teacher, and thus I become a children’s yoga teacher. I set up an after school club but found the work frustrating primarily because of my realisation that yoga needed to be taught as part of the school day for children to benefit most.
Nevertheless word of my work had spread and one day I was asked to teach yoga to children in a Special Needs School in East London. That day was a turning point in my life. Despite all my experience I stood there not knowing what to do while this group of children were going absolutely crazy, at one time cussing at me and throwing shoes around – it was chaos. I tried various activities, all to no avail. Then, amazingly, with one specific activity (it was Sun Sequence), they were suddenly hooked… and I even got them to do a relaxation. The transformation was astounding. I came out of there that day, sat in the car and cried tears of joy that I could make such a difference. That was a Tuesday Morning in 1999 and I have taught there every Tuesday ever since. Over time the school has become a beacon school for teaching children with autism. This means that for more than a decade I have been developing teaching approaches for teaching yoga to children with autism. I am now regarded as a specialist in teaching yoga to autistic children. I am very proud of that.
In the last few years I have been fortunate to have taught continuously in the same nucleus of schools. This means that I am there on a specific day every week, every term, every year. It also means that I have had to be creative and develop fun and interesting activities or risk the children’s boredom. I have taught yoga in schools as part of the integrated school day for more than a decade now and have developed many approaches and activities that the children love.
One of those activities has now been turned into a book called Frog’s Breathtaking Speech. Now my enthusiasm for writing knows no bounds and I am busy with three new books that will enable me pass on my considerable expertise to others. Frog’s Breathtaking Speech – and incidentally The Very Hungry Caterpillar, The Gruffalo, and Going on a Bear Hunt – all make terrific stories to embed yoga postures in.
What inspired you to write this wonderful book?
I have been using Frog’s Breathtaking Speech in children’s yoga lessons for many years. The story grew out of the need to increase children’s awareness of their breath and, more importantly, how to apply it in stressful situations. Situations such as dealing with exams, spelling and table tests, being bullied, tension, headaches and anger, and of course performing or presenting to their peers and parents in assembly.
Although, as an adult, I had experienced the benefits of yoga breathing techniques I had honestly found them dry and unexciting. If I was to grab the children’s attention I needed to teach breathing techniques in a way that was fun and relevant. My strategy was to use the story in a yoga/drama format and it was an immediate success.
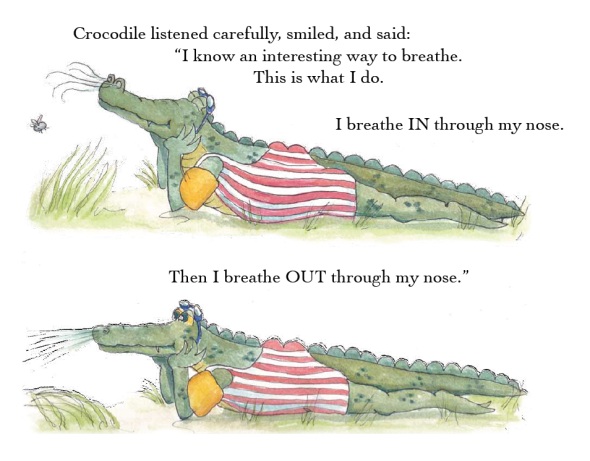
I would set out the yoga mats in a circle in the hall. As many children as possible would be given the opportunity to be Frog. I would ask for sad faces and then ask for less sad faces as the story unfolds. The other characters, Crocodile, Lion, Humming Bee and Mr Gumble the Woodchopper, would be played by the whole class. To keep the “chorus” in unison I would hold up placards in pantomime style saying, “Why so sad Frog?” and “I know an interesting way to breathe”. We have also performed Frog on stage to great applause.
I think there are several reasons why this approach worked well, including:
- there was sufficient repetition for everyone to be able to join in;
- it was obviously great fun;
- the children were learning the techniques in a fun and relevant context;
- children found the characters interesting.
Looking back I think that one of the main factors that inspired me to turn the yoga play into a book was the feedback from the children. I have lost count of the amount of times that children would tell me how they had used the techniques to deal with incidents in their lives. Problems ranging from being angry at siblings who stole their sweets or broke their toys, to being the calming influence in big family arguments. My two favourites will always be: the nine-year old boy who was terrified of the dentist and who quietly sat in the waiting room, and ultimately the dentist’s chair, practising his Crocodile Breath to calm himself; and the ten year old girl, who was angry with her parents, who would go to her room and practice Woodchopper Breath every day for three weeks, who eventually came and told the class teacher and me that that she had Haaaa’d out her anger.
The other main factor that inspired me to turn the play into a book was, simply, to get it out there. If this story helped the children that I taught it would help all children.
 Can you tell us about your collaboration with the illustrator,
Can you tell us about your collaboration with the illustrator,
Sarah Peacock?
I have worked with Sarah Peacock in her Hertfordshire Primary School for five years. Sarah would come into in the yoga lesson with her class and over the years had been involved with Frog’s Breathtaking Speech on many occasions. She knew the story very well and how much the children liked it.
Examples of Sarah’s amazing illustrations were displayed around school. Often over lunch she had talked about her dream of being an illustrator. When I finally wrote the story as a book, I asked her to illustrate and she came up with the wonderfully timeless and charming illustrations that make the book so readable.
Where did the character of Frog come from?
Frog came about for a variety of reasons.
Firstly, children can stay in Frog Posture easily for longish periods without too much discomfort (and it’s great for their knees and hips). Secondly, I like Frog characters – they make me laugh; and thirdly, there is a long history of Frogs (and Toads) in children’s literature – for example, The Frog Prince and The Tale of Mr. Jeremy Fisher.
I saw Frog as a character that boys and girls could relate to because he was honest about his fears. I think they could also relate to his courage in taking action, facing his fears and achieving a victory.
I suppose he is based on many of the children that I have taught and if I am being honest there’s a lot of me in Frog. (Well, even grownups need to calm themselves and get angry sometimes.)
Can you describe scenarios in which the different breathing techniques would be especially useful?
I think that being a child nowadays is stressful. I have already mentioned my two favourite examples of how techniques from the story have helped. However as educationalists we are constantly aware that the children in our care are travelling through a minefield of emotional problems in different areas of their lives.
For example children are dealing with major blows within the Family like divorce; separation from parents; death of a family member or friend or pet; worries about family’s financial situation; worries about a family member’s health; or perhaps a new baby brother or sister has arrived.
At school children are often anxious about their lack of specific skills, being bullied, tests, SATs, how to deal with an overload of activities, a belief that they do not have enough friends, lack of self-esteem, fear of failure, and even fear of success.
On the social side, children can be anxious because they may see themselves not “in” with the right crowd, too fat, too thin, too tall, too small, too ugly and so on.
I believe the social pressures on children – in or out of school – are immense today and we need to teach them all manner of strategies to help them deal with the pressure. Yoga and breathing techniques being at the top of the list.
The four strategies that are taught in Frog are:
- Crocodile Breath. Situations where children could apply the technique are: tests, exams, sports day, making speeches to peers and parents, going to the dentist, finding courage.
- Humming Bee Breath. Situations could include: headaches, feeling tense, panicky in the middle of a busy shopping centre at Christmas.
- Woodchopper Breath. Situations could include: venting anger or frustration.
- Lion Breath. Situations could include: strengthening voice or loosing tension.
How can this book be used with children with special needs?
Frog can be used with all children and that includes many children with special needs.
Used purely as a story, Frog is highly engaging, the illustrations compelling, and there is sufficient repetition to help reinforce readers and invite anticipation. There are also ample opportunities to compare the Frog’s experiences to the children’s if the children are at a suitable level.
On a higher level, if you are reading the book to children and encouraging them to practice the postures there is a lot to be gained. Firstly, the children will benefit from increased flexibility and better muscle tone. The big reward, however, is that yoga postures can help children with Sensory Processing Disorders.
Many children with autism, for example, have Sensory Processing Disorders which affects their Vestibular, Proprioceptive and Tactile systems. This is a vast subject that I will deal with elsewhere. Suffice to say that yoga can go a long way to identify any extremes in a child’s sensory behaviour and provide strategies to help regulate their nervous systems away from those extremes.
Using the story in a yoga/drama format also creates opportunities to work on speaking and listening skills and other communication skills like, for example, projecting the voice. Also social skills such as taking turns, waiting or applauding another child will come up when you use this story.
One massive benefit of using the story with children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD), for example, is the opportunity to be acting out different emotions. Frog becomes less sad as the story progresses. In fact, emotions range from sad to happy, scared to brave, beaten to successful. A great excuse to give those face muscles a good workout.
Finally, if you are using the story in a yoga/drama format and including the breathing techniques then you are encouraging the children to be “in the moment” – a well hackneyed yoga term, I know, but totally appropriate for children on both extremes of the hyperactivity scale who need to find “that middle ground of alert interest where they are not overwhelmed or underwhelmed” (Sher, B. 2009 p. 22).
Copyright © Singing Dragon 2011.
 Make sure not to miss Singing Dragon’s latest UK Complete Catalogue. If you have not yet received a copy, please sign up for our mailing list and we’ll send a free one out to you ASAP.
Make sure not to miss Singing Dragon’s latest UK Complete Catalogue. If you have not yet received a copy, please sign up for our mailing list and we’ll send a free one out to you ASAP.







 Singing Dragon was thrilled to attend the 16th annual conference of the National Qigong Association (NQA) in Valley Forge, Pennsylvania, USA, from August 19-21.
Singing Dragon was thrilled to attend the 16th annual conference of the National Qigong Association (NQA) in Valley Forge, Pennsylvania, USA, from August 19-21.



 Singing Dragon received the Gold prize in the Enlightenment/Spirituality category for
Singing Dragon received the Gold prize in the Enlightenment/Spirituality category for