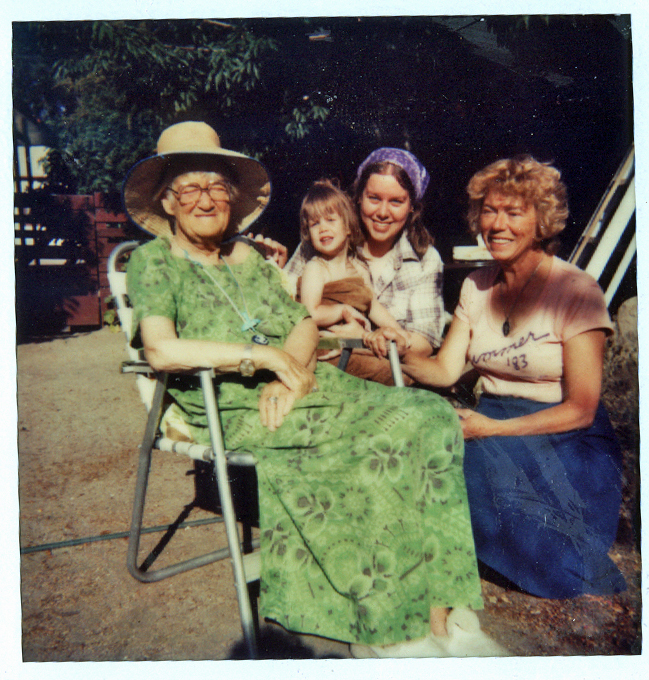Marte Brengle is the novelist Evelyn Eaton‘s eldest grandchild and only granddaughter. She is also a writer, and manages the family publishing company, Logan Books. Here, she shares some personal memories of her remarkable grandmother and reflects on the personal significance of Eaton’s books, Go Ask the River and I Send a Voice.
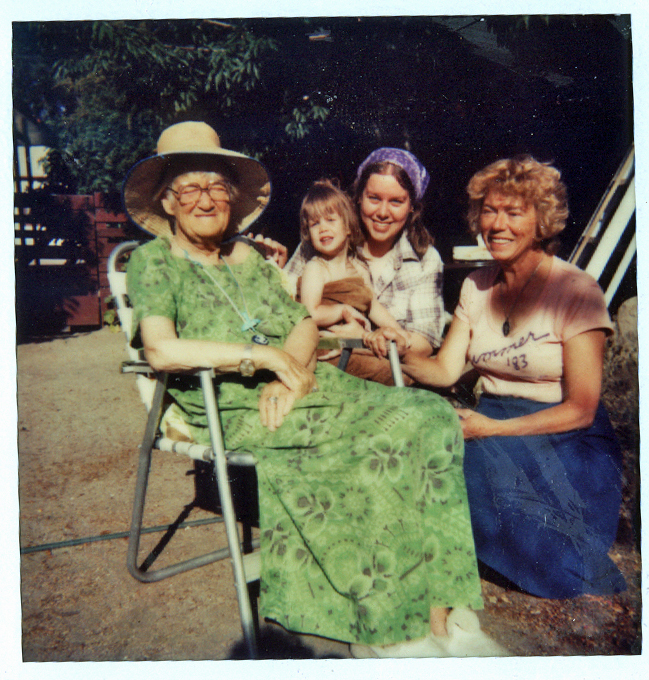
Photo: “Four generations of women – Gran, my daughter Meghan, me and Mom – taken just a few months before Gran died. I think it represents all that was happy about our relationships.” (Courtesy of Marte Brengle)
Your grandmother, the novelist Evelyn Eaton, lived an enormously rich and varied life. How much did all this come through when you were growing up? Or are you still finding out about her?
I didn’t know a lot about Gran’s life until I read her autobiography in 1974. She told us some stories about her life, but there was a lot she didn’t talk about. My third novel is based on her life, my mother’s, and my own, and in re-reading Gran’s autobiographical books I have had to extrapolate and fill in the blanks a lot. I wish I had thought to ask her to annotate a copy of her autobiography, because as I’ve re-read it this past year I can see she put in some very subtle hints about the parts of the story she left out. In many ways, Go Ask the River is Gran’s story just as much as it is Hung Tu’s. The paralells are quite striking. I named my son after her father, since my son was born 60 years almost to the day after his namesake was killed at the battle of Vimy Ridge.
Evelyn’s books ranged across wide territory. The two in the Singing Dragon list cover very different worlds – the life of the Chinese Tang dynasty poet Hung Tu, and initiation into Native American Sweat Lodge ceremonies. Do you think that for her there was a connection between the two?
My grandmother was always interested in the supernatural world, and the ways in which spiritual beliefs shape people’s lives. She could see the supernatural quite clearly. I think she believed she was the reincarnation of Hung Tu, and also the descendant of Native Canadians, so she herself provided the connection between the two. She always said: “There are many paths to the center, and all of them are true.”
Her book about ancient China brings to life a completely different world, and as Chungliang Al Huang’s Foreword recounts, was based on a strange and intense experience she had while a war correspondent in China. And of course as a Native American Medicine Woman, she must have carried much information she could not talk about. Was this obvious in meeting her? What was she like as a grandmother?
Gran always seemed to understand me, and what was in my mind, far better than my mother did. Even though we weren’t together much (separated by geography), I always felt I could tell her anything and ask her anything and she’d understand what I meant even if I didn’t express it properly. She understood my brothers in the same way. To me it was obvious that she was deeply connected to the supernatural world, and it was clear to some other people as well. I don’t know how she was perceived by the world at large, but clearly she was a remarkable person and would have gotten anyone’s attention.
I remember in the spring of 1975, my husband and I took the train from our home in Kansas to visit Gran in California. Gran could tell the future with a pack of ordinary playing cards and she was very good at it, although it wasn’t something she liked to do because of the possibility of seeing something bad. I asked her to read the cards for me. At the end of the process, the person whose future is being told is asked to pick three cards while thinking of a question that can be answered yes or no (without asking it out loud). My silent question was “Will I have a child within two years?” Gran looked over the cards and immediately said “The answer is yes, and if you’re asking about a child, it will be a boy.” When I was expecting my first child, my doctor – who didn’t to ultrasounds, amniocentesis or any of those things – told me she thought I was expecting a girl, so I went through the whole pregnancy thinking I’d have a daughter. But, as Gran predicted, the child was a boy, born almost exactly two years after the prediction.
Did she continue to be interested in China and the Oriental arts throughout her life?
I think she did. She always had Chinese artifacts in her homes, and she burned Chinese incense in her writing room before she began burning sage. I inherited some of the embroidered silk panels she brought back from her trip as a war correspondent. They’re faded now, but I keep them on the wall as a reminder of Gran.
Do you know what took her to the immersion in the Arapaho healing traditions that occupied the last years of her life?
If you read her autobiography, The Trees and Fields Went the Other Way, you can see how she encountered Native spirit guides very early in life. She always connected with people, and I think when she moved to California it was only natural for the Paiutes to come to trust and accept her. It wasn’t an easy path, because they were quite rightly wary of revealing too much to outsiders (and indeed, the Sweat Lodge to which she once belonged has been closed to outsiders for many years now, as Eagle Man’s descendants think differently about the inclusion of non-Indians).
I Send a Voice is such a powerful account of the process of change and becoming. Did her relationship with the family change also during that time?
We were separated by great distances while this was happening – my family in the midwest and Gran in California. She didn’t talk about it much in the beginning, so we weren’t affected by her new understanding of the universe. After my mother and two younger brothers moved to California, they got involved in the Sweat Lodge and it was clear that it had a great personal connection for them as well. I attended one Sweat Lodge ceremony and was so overwhelmed by it that I turned down later invitations to join in.
What happened to her pipe after her death?
My mother inherited Gran’s pipe. She talked about giving it to other people several times over the years, but my brothers and I always maintained that it should stay in the family. My mother left no instructions about Gran’s pipe when she died, so it remains with my second brother, who bought the house Mom lived in and took care of her during her last days. My brothers and I have talked a bit about what should happen to it but we have never really decided one way or the other.
You are also a writer – how did you grandmother and her books inspire your own writing?
Although I had done a lot of technical writing and had written magazine articles, reviews and the like, when I first tried my hand at writing a novel it took me more than twenty years to complete it! The good thing about that is that I was a much better writer by the time I finally got it done. My two published novels are stories about people trying to make peace with their pasts. No high drama and flashy action, just human stories and human nature. My third novel is based on my grandmother’s life, my mother’s and my own. It will be a very long book, covering the time span from 1902 to about 1980.
Gran’s stories were also about human problems and human nature. With Go Ask the River, especially, she went deeply into the human heart. I did not start out thinking I was going to be a writer. I tried a lot of other things before going back to the novel I’d half-heartedly started. I realized there was a better story to be told than what I’d written, and I drew on some of the advice Gran gave me when I went back to work on it. She said you have to know your characters almost as well as you know yourself. I didn’t quite manage that, because my characters kept suprising me by saying and doing things that I didn’t consciously have in mind, but I did try to keep them, and what they said and did, as realistic and true to life as I possibly could.
Evelyn Eaton (1902-1983) was born in Montreux, Switzerland to Anglophile Canadian parents, and educated in England and France. She began writing while still in her teens; her first collection of poems was published in England in 1923 (the same year that she was presented at court) and her first novel in 1925. She became an American citizen at the age of 42, and was a war correspondent in China, Burma and India in 1945, then a lecturer at Columbia University from 1949 to 1951. Partly Native American (related to the Algonquians of New Brunswick, Canada) her later years became increasingly focused on Native American culture and mysticism. She wrote thirteen novels, five volumes of poetry, two collections of short stories, and seven other books. For many years she was a contributor to The New Yorker and other journals.
Copyright © Singing Dragon 2012.